rwlock和spinlock实现
#spinlock #lock #sparse
一下源码分析基于linux 6.6.1
sparse
https://lwn.net/Articles/689907/
#define acquire __context__(x,1)
https://hackmd.io/@sysprog/linux-sync
https://gcc.gnu.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=59856
https://lwn.net/Articles/689907/
https://lwn.net/Articles/109066/
https://sparse.docs.kernel.org/_/downloads/en/doc-ptrlist/pdf/
rwlock
__raw_read_lock
include/linux/rwlock_api_smp.h
static inline void __raw_read_lock(rwlock_t *lock)
{
preempt_disable();
rwlock_acquire_read(&lock->dep_map, 0, 0, _RET_IP_);
LOCK_CONTENDED(lock, do_raw_read_trylock, do_raw_read_lock);
}
include/linux/rwlock.h
# define do_raw_read_lock(rwlock) do {__acquire(lock); arch_read_lock(&(rwlock)->raw_lock); } while (0)
include/linux/compiler_types.h
这里的__context__还有__attribute__((context(x,1,1)))为sparse实现,主要功能是操作context的引用计数
/* context/locking */
# define __must_hold(x) __attribute__((context(x,1,1)))
# define __acquires(x) __attribute__((context(x,0,1)))
# define __cond_acquires(x) __attribute__((context(x,0,-1)))
# define __releases(x) __attribute__((context(x,1,0)))
# define __acquire(x) __context__(x,1)
# define __release(x) __context__(x,-1)
# define __cond_lock(x,c) ((c) ? ({ __acquire(x); 1; }) : 0)
include/linux/rwlock_types.h
typedef struct {
arch_rwlock_t raw_lock;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_SPINLOCK
unsigned int magic, owner_cpu;
void *owner;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LOCK_ALLOC
struct lockdep_map dep_map;
#endif
} rwlock_t;
spinlock
spinlock的实现类似于银行业务办理系统,每个客户来办理业务的时候需要先取号,之后等银行叫号再到指定柜台办理业务。
arch_rwlock_t结构体内的owner表示当前可持有lock的线程,next表示下一个线程拿到的号码,系统内部有一个全局的arch_rwlock_t来来显示当前作业系统的状态
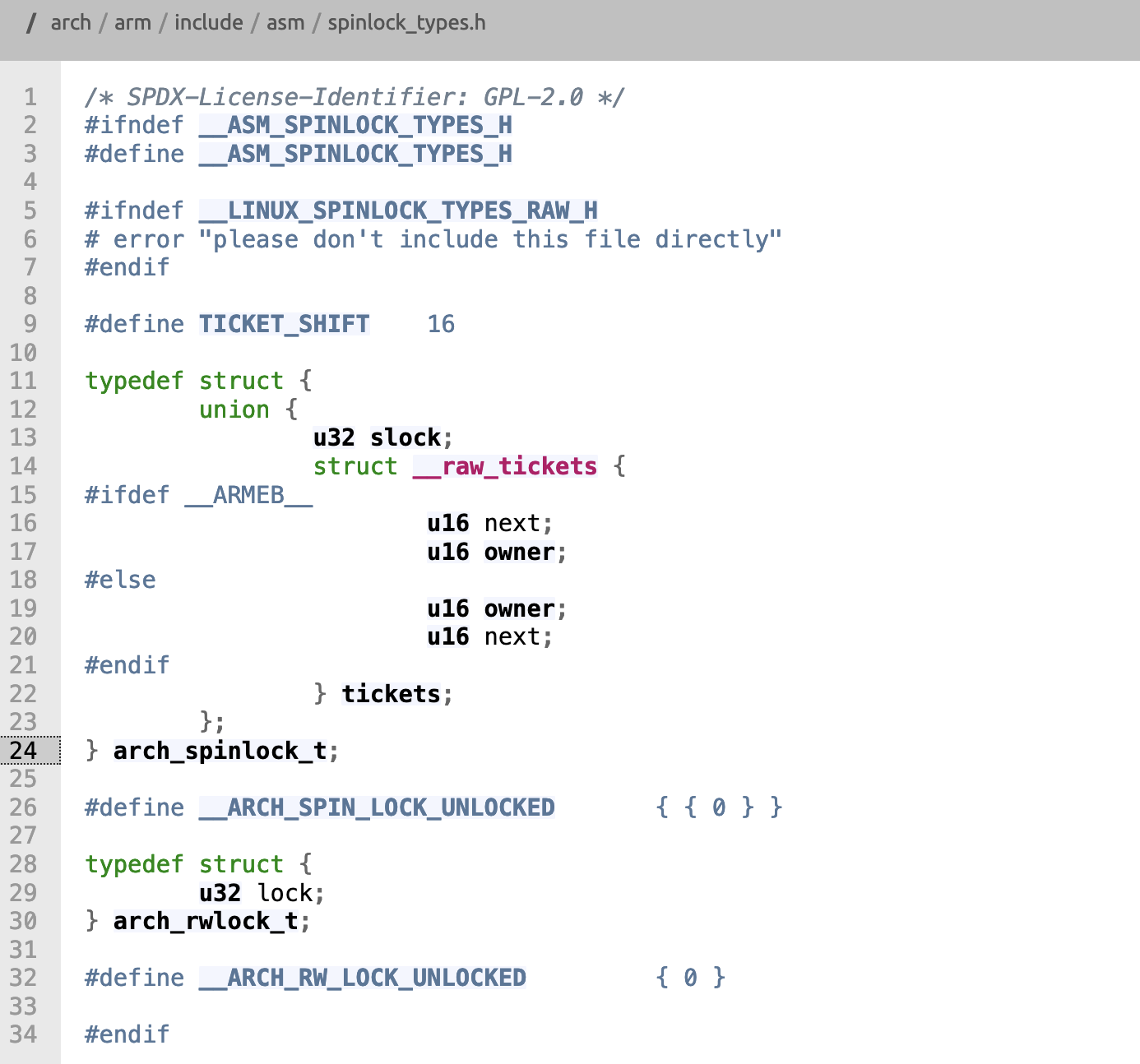
arch_spin_lock实现
每一个想要作业的线程需要先同步一份系统的arch_rwlock_t到本地,系统的next会+1,表示下一个线程拿到的号码,在线程拿到号码之后会不定时的更新本地记忆的owner,直到owner等于拿到的号码牌就获取lock得到执行权
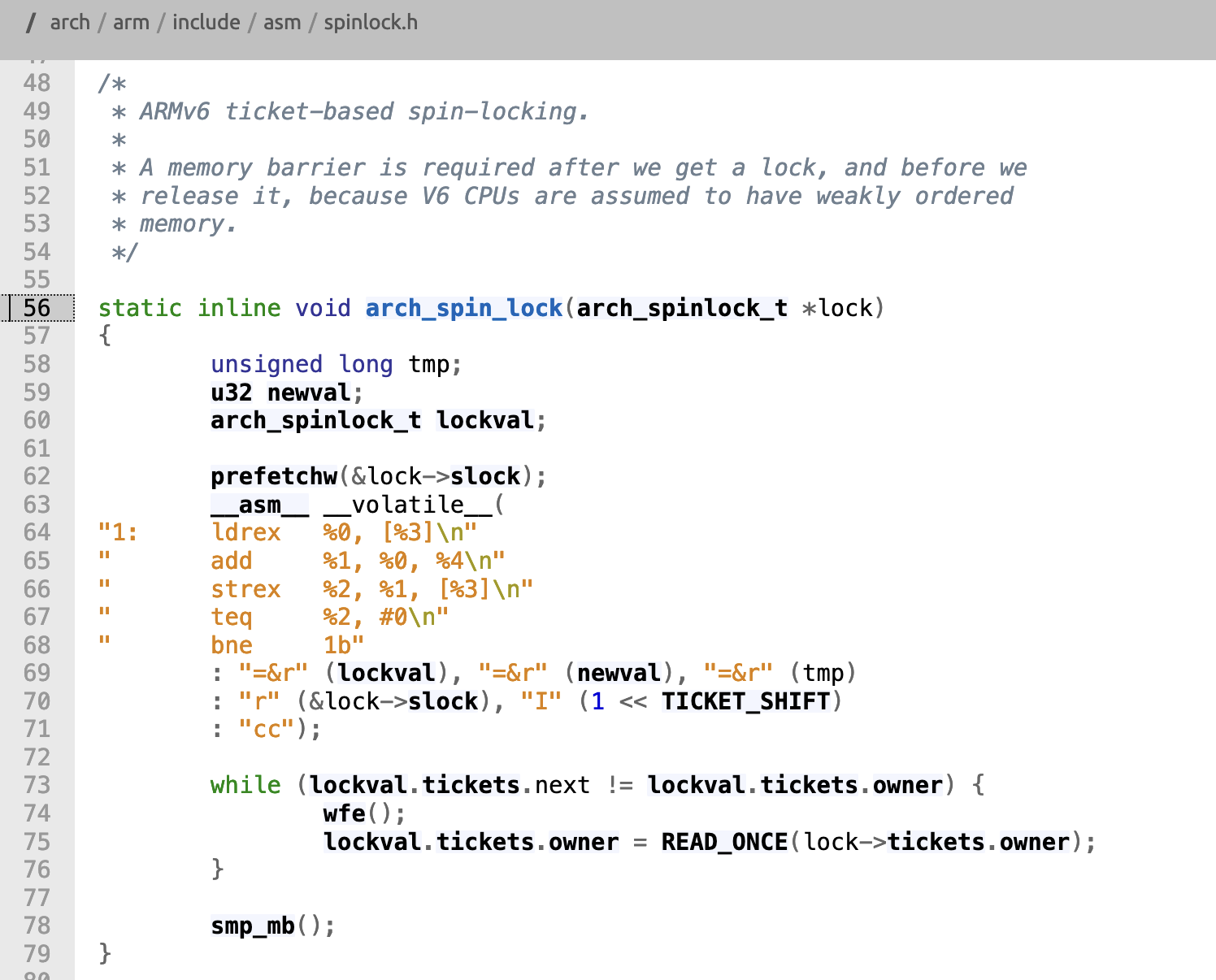
以上汇编代码简化成cpp功能如下
static inline void arch_spin_lock(arch_spinlock_t *lock) {
arch_spinlock_t local_lock;
local_lock.slock = lock->slock; /* 1 */
lock->tickets.next++; /* 2 */ //系统下一个取号码+1
// 当发现系统当前可办理业务的编号和自己取的号码一致的时候可以直接办理业务,否则等待,不时抬头检查
while (local_lock.tickets.next != local_lock.tickets.owner) { /* 3 */
wfe(); /* 4 */
local_lock.tickets.owner = lock->tickets.owner; /* 5 */ // 抬头更新记录一下系统最新的办理人编号
}
}
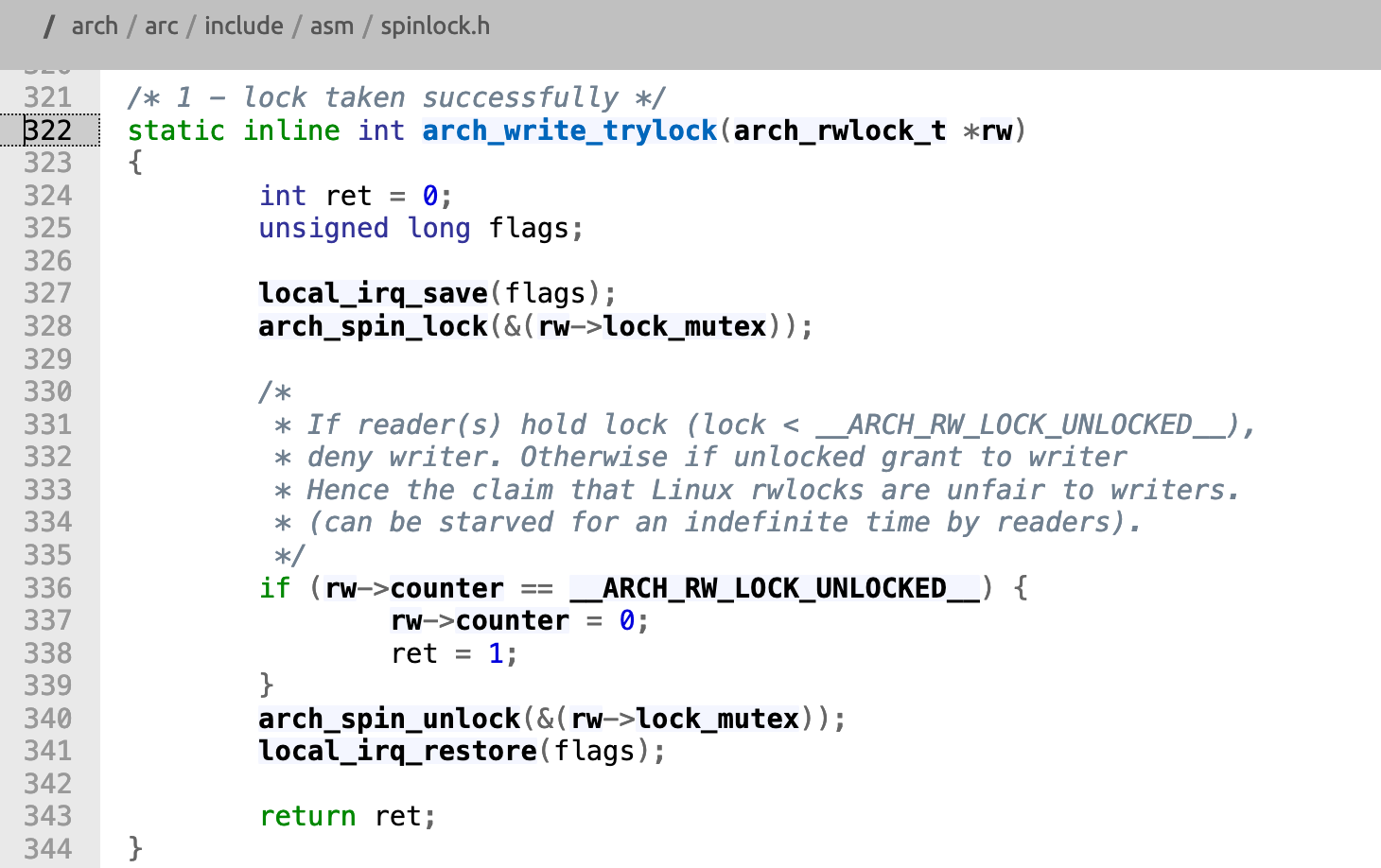
arch_write_trylock的实现
这里使用AT&T格式的基于arm指令集的assembly language code snippet,
这里的%0是contended,%1是res,基于asm申明的变量occur order,其中
=r constraint indicates that %0 (result) is an output operand, By adding & to the constraint, we are indicating that %0 is early-clobbered.
Theldrexandstrexeqinstructions are part of ARM's exclusive access instructions, which provide a way to perform atomic read-modify-write operations.
这里进程想要持有写锁需要确认当前lock的是否被占用(如果lock=0,则没有被占用),如果没有被占用直接先将lock值设置成0x80000000,然后就执行smp_mb
smp_mb();: This is a memory barrier, which ensures that all memory operations before the barrier are completed before any memory operations after the barrier. Memory barriers are used to control the order of memory accesses and ensure proper synchronization.
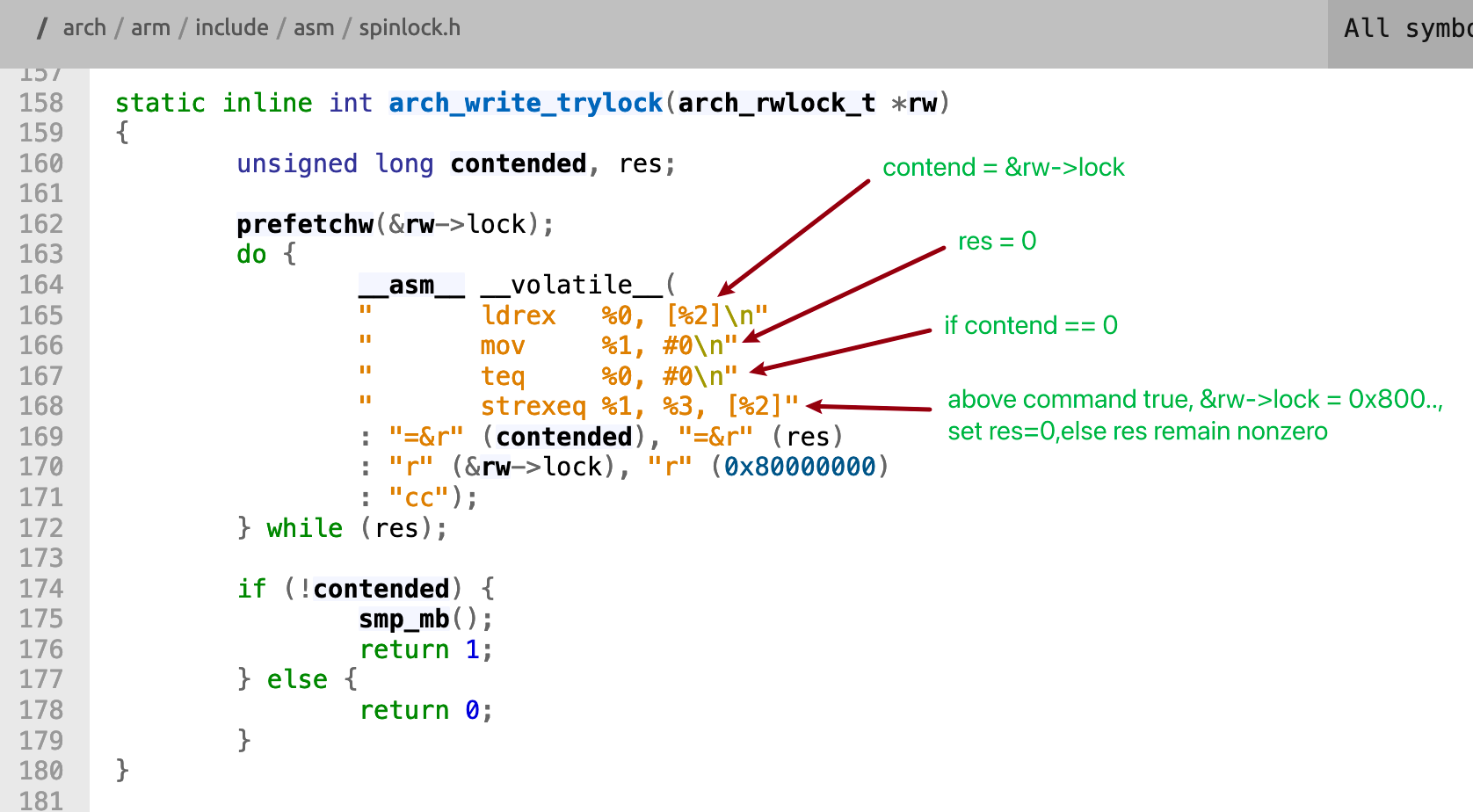

对于arch_write_trylock的实现arm架构由于有asm代码比较难懂,可参考arc架构的相关实现,原理基本类似的